Game-Changing Solid-State Batteries Coming to Market Soon
by Alfred Newman
South Korean battery cell manufacturer Samsung SDI accelerated its schedule to introduce solid-state batteries at scale. Their hopes lay on a pilot line under construction near Seoul.
Samsung SDI began building the pilot line as ‘S-Line’ at its research and development centre in the South Korean city of Suwon in March. The company expects to produce its first solid-state cells from early 2023. In a call earlier in May-2022, Samsung said the pilot project would accelerate the commercial introduction of solid-state cells, previously targeted for 2027. “Through checking our technological viability and securing know-how for mass production, we will speed up the timing for mass production,” UPI news agency quotes from the call.
About solid-state batteries:
Solid state batteries have already been in use for years in pace makers as well as RFID and wearable devices. The next generation of solid state batteries, for mass market adoption to replace current lithium ion technology, is nearing launch from labs globally, from big players like Samsung, Toyota, Panasonic, BMW, etc. to small players like Volt Carbon Technologies — the technology is available for licensing / purchase from various sources and provides immense opportunity going forward.
Fact: All EV manufacturers will transition to solid state lithium ion batteries for new vehicles within the next several years; the results will eventually mean recharging of cars approaching the same time required to fill a gas tank, lighter batteries, stable (non-volatile) batteries, and solid state lithium batteries will last decades, instead of years. Solid state batteries will eventually become ubiquitous and found in all sizes for most everything.
A lithium-ion battery is composed of cathode, anode, separator and electrolyte. Current Lithium ion batteries on the market currently (such as those used in smartphones, power tools and EVs) use liquid electrolytes between the anode and cathode. On the other hand, a solid-state battery uses solid electrolyte, not liquid.
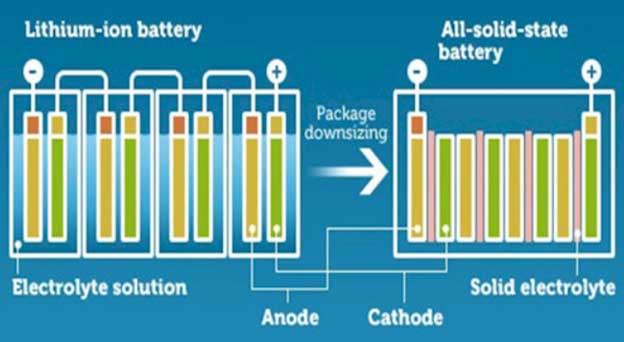
What users most worry about a lithium-ion battery is safety. The current Li-ion battery has a risk of battery damage such as swelling caused by temperature change or leakage caused by external force since it uses liquid electrolyte solution. However, a solid-state battery with solid electrolyte shows improved stability with a solid structure, and increased safety since it maintains the form even if the electrolyte is damaged. Also, after repeated recharging liquid electrolytes are more prone to develop dendrites which can diminish life and increase fire risk — not so with solid state.
A solid-state battery has higher energy density than a Li-ion battery that uses liquid electrolyte solution. It doesn’t have a risk of explosion or fire, so there is no need to have components for safety, thus saving more space. Then we have more space to put more active materials which increase battery capacity in the battery.
A solid-state battery can increase energy density per unit area since only a small number of batteries are needed. For that reason, a solid-state battery is perfect to make an EV battery system of module and pack, which needs high capacity.
##
Content above may contain forward-looking statements regarding future events that involve risk and uncertainties. Readers are cautioned that these forward-looking statements are only predictions and may differ materially from actual events or results. Articles, excerpts, commentary and reviews herein are for information purposes and are not solicitations to buy or sell any of the securities mentioned.

